
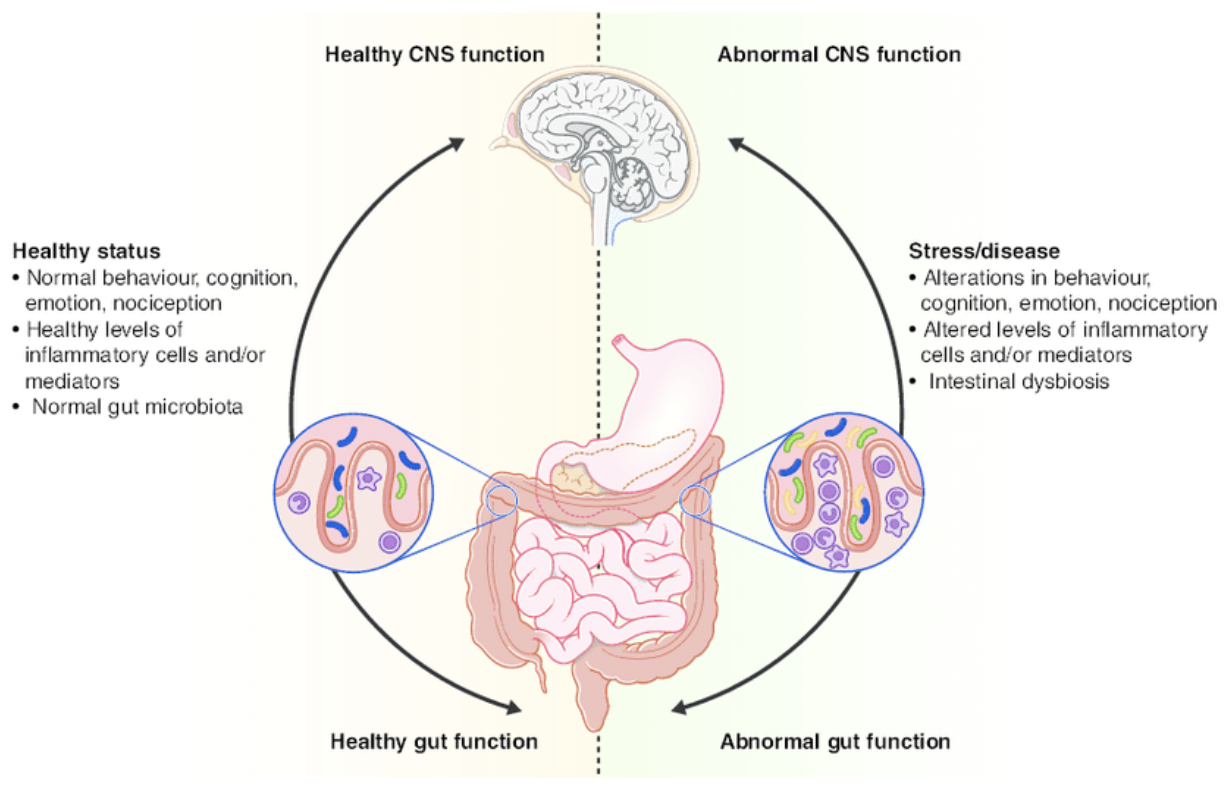
Have you ever heard of the saying ‘you are what you eat’? Well according to research this statement does seem to hold a valid argument in scientific literature. Food plays a vital role in providing the body with the essential nutrients that impact an individual’s mental health and physical well-being. A person’s diet can largely impact the brain’s structure and function, how the brain modulates stress responses, immunity, and the endocrine system (Muscaritoli., 2021). The stomach itself has been referred to as the second brain. The gut-brain axis (GBA) is a communication system that maintains homeostasis within the gastrointestinal system and is suspected to have effects on motivation and cognitive functions (Carabotti et al., 2015).
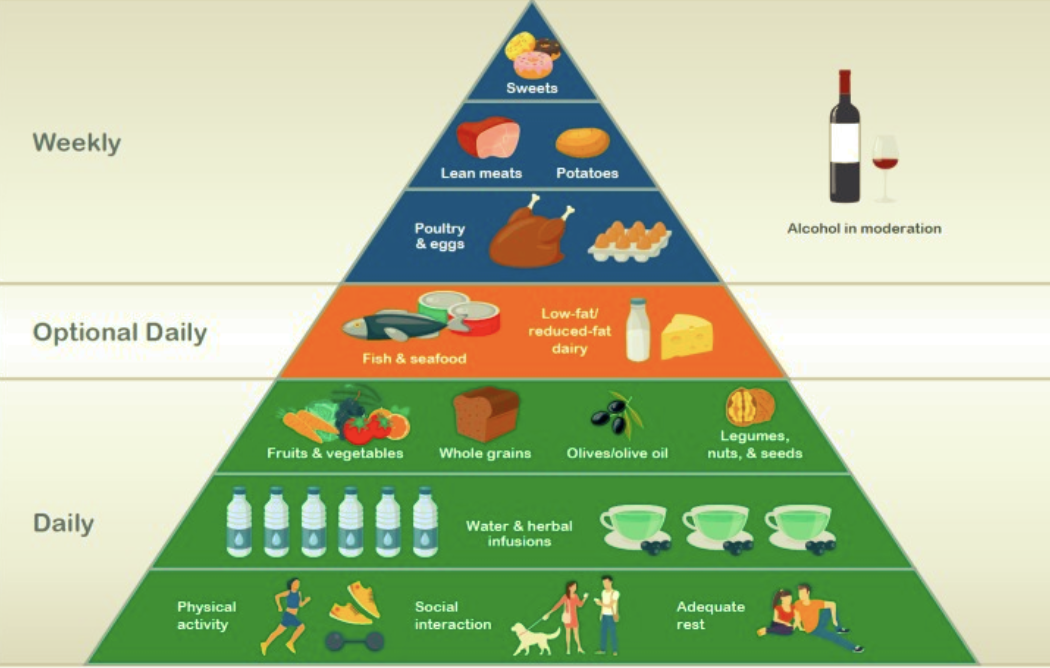
What is a Healthy Diet?
There are so many different diets out there, that it can be hard to decide which diet can be the most beneficial. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends balancing macronutrients and micronutrients, limiting trans and saturated fats, and increasing fruits and vegetable intake (Cena & Calder., 2020).
Macronutrients Vs. Micronutrients
Macronutrients include fat, protein, and carbohydrates, by balancing these nutrients this will provide a positive impact on a person’s health (Venn., 2020). A person’s diet can largely affect homeostasis and when compromised can create an environment where disease or illness can arise.
Micronutrients include vitamins and minerals, which are required in small amounts to assist with optimal functioning in proteins and enzymes (Chen., 2018).
Micronutrients & impact on immune system (Maggini, Pierre, & Calder., 2018)
- Vitamin B6 – Regulates inflammation, required in synthesis of amino acids, and has a role in antibody production.
- Vitamin B12 – Assist with immune cell functions.
- Vitamin C – An antioxidant that protects you from reactive oxygen species (ROS), promotes antibody and collagen production.
- Vitamin E – Provides support for fat-soluble antioxidants, protects cells from free radicals.
- Vitamin D – Assists immune system cells in differentiating and proliferation, helps to regulate antimicrobial proteins that can kill pathogens.
- Vitamin A – Supports maintenance of structure and function for mucosal cells which are the first line of defence in immunity such as skin, respiratory tract.
- Iron – Regulates cytokine production, helps kill harmful bacteria.
- Zinc – Has antioxidant properties against ROS, provides support for maintaining skin and mucosal membranes, required for T cell development and activation.
- Folate – Maintains innate immunity (first line of defence).
References
Carabotti, M., Scirocco, A., Maselli, M. A., & Severi, C. (2015). The gut-brain axis: interactions between enteric microbiota, central and enteric nervous systems. Annals of gastroenterology, 28(2), 203–209.
Cena, H., & Calder, P. C. (2020). Defining a Healthy Diet: Evidence for The Role of Contemporary Dietary Patterns in Health and Disease. Nutrients, 12(2), 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12020334
Chen, Y., Michalak, M., & Agellon, L. B. (2018). Importance of Nutrients and Nutrient Metabolism on Human Health. The Yale journal of biology and medicine, 91(2), 95–103.
Maggini, S., Pierre, A., & Calder, P. C. (2018). Immune Function and Micronutrient Requirements Change over the Life Course. Nutrients, 10(10), 1531. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10101531
Muscaritoli M (2021) The Impact of Nutrients on Mental Health and Well-Being: Insights From the Literature. Front. Nutr. 8:656290. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.656290
Venn B. J. (2020). Macronutrients and Human Health for the 21st Century. Nutrients, 12(8), 2363. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12082363
Gillian McKeith (2006). You Are What You Eat Book. https://gillianmckeith.com/books/eat/
Photos:
https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Impact-of-the-gut-microbiota-on-the-gut-brain-axis-in-health-and-disease-A-stable-gut_fig3_258198236
Cena, H., & Calder, P. C. (2020). Defining a Healthy Diet: Evidence for The Role of Contemporary Dietary Patterns in Health and Disease. Nutrients, 12(2), 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12020334

